Dont wan't to watch the video, read the text instead.
What is Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio?
The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio) is the ratio for valuing a company that measures its current share price relative to its per-share earnings (EPS). The price-to-earnings ratio is also sometimes known as the price multiple or the earnings multiple. P/E ratios are used by investors and analysts to determine the relative value of a company's shares in an apples-to-apples comparison. It can also be used to compare a company against its own historical record or to compare aggregate markets against one another or over time. There are primarily two types of P/E Ratio: trailing P/E ratio and forward P/E ratio. Forward P/E ratio tries to predict the earnings of a company basis trends and analysis.
The formula for calculating P/E ratio is:
PE Ratio = Market Value per share ÷ Earnings per share
A high P/E ratio could mean that a company's stock is over-valued, or else that investors are expecting high growth rates in the future. Companies that have no earnings or that are losing money do not have a P/E ratio since there is nothing to put in the denominator.
Earnings per share (EPS) is calculated as a company's profit divided by the outstanding shares of its common stock. The resulting number serves as an indicator of a company's profitability. It is common for a company to report EPS that is adjusted for extraordinary items and potential share dilution. The higher a company's EPS, the more profitable it is considered to be.
The formula for calculating EPS ratio is:
EPS = (Net Income - Preferred Dividends) ÷ Common Shares Outstanding
To calculate a company's EPS, the balance sheet and income statement are used to find the period-end number of common shares, dividends paid on preferred stock (if any), and the net income or earnings. It is more accurate to use a weighted average number of common shares over the reporting term because the number of shares can change over time.
P/E Ratio and Investing in Mutual Funds:
In mutual funds, the P/E ratio of a scheme is arrived at by using a weighted average of all the underlying stocks. It is the average of the P/E ratio of all the stocks that the fund’s portfolio contains, proportionate to their allocation within the portfolio. For example, if a scheme is holding INR 20,00,00,000 worth of stock A and INR 30,00,00,000 worth of stock B, the total holdings equal INR 50,00,00,000. Here, 40 percent of this total is held in stock A and 60 percent in stock B. If the P/E ratios of the stocks are 10 and 12, respectively, the fund's P/E ratio equals 40 percent of 10 plus 60 percent of 12 which is therefore (0.4*10) + (0.6*12) = 11.2
A high P/E would indicate that the mutual fund investment holds mostly stocks that are quoting a valuation premium. This indicates a preference for growth and growth-oriented businesses. In a growth-based approach, the fund manager does not mind paying a high price for stocks that are displaying good growth in profitability.
On the contrary, a low P/E signifies a value-conscious approach. Here, the fund manager is more comfortable investing in stocks that are currently not in demand or where the stock price has been beaten down disproportionately to the fundamentals of the company.
The graph below compares the movement of the Nifty 50 index with its 1 year forward P/E ratio as an illustration:
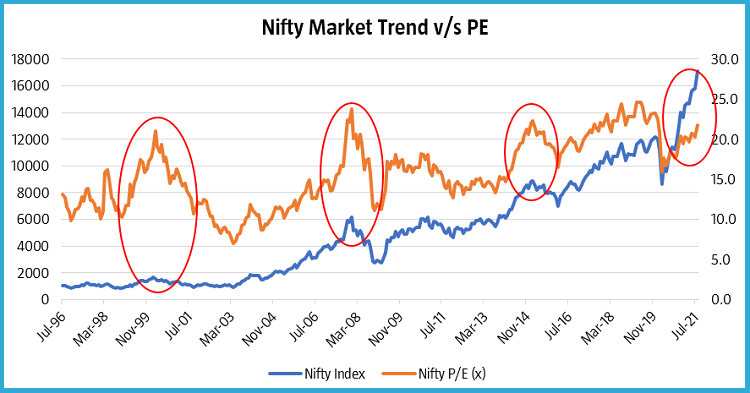
Source: Bloomberg
Disclaimer: The data/statistics are given to explain general market trends, it should not be construed as any research report/research recommendation.
As can be observed here, the Nifty index has fallen when the P/E has risen above a level of 20. However, we can see that the Nifty levels have started to rise with the fall in P/E ratio. Therefore, an undervalued market could be considered as a choice for equity investment; however, allocation to equity mutual fund portfolios having exposure to quality companies and diversification could benefit over long term.
Key Takeaways
- Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio helps in understanding if a particular company is overpriced or underpriced
- It also helps in comparing a company with its past record and track its growth
- In mutual funds, P/E ratio can be used to determine a growth-based or value-based investment style
- Investors can refer to the P/E ratios of different mutual fund schemes to suit their investment goals and patterns
- The ratio should be not be seen in isolation and should be considered with other factors such as quality of companies and diversification of portfolios



