Dont wan't to watch the video, read the text instead.
Sharath, an enthusiastic entrepreneur, has started his business immediately after his graduation. He is running his business for the last 2 years and the business has started doing reasonably well in the last couple of months resulting in positive cash flows. Since he is left with some surplus cash in his business as well as in his hands, he would like to invest the same for the rainy day. When he visits the bank, he discusses the investment options with the relationship manager and requests for opening up Fixed Deposit account. The relationship manager suggests a category of mutual funds instead of bank deposits, but Sharath is concerned that investing in equity would be too risky.
Another wrong perception which people carry about mutual funds is that Mutual Fund means Equity Mutual funds and take exposure only in equity/stock markets.
Mutual funds are investment vehicles which helps the investors to invest in marketable securities. Marketable securities could be Equity/Stocks, Bonds/Debt and Gold. When a mutual fund is launched, it could be a fund which invests majority in equity stocks or Bonds or Gold or combination of the asset classes.
Broadly mutual funds could be categorized into 3 types;
- Equity Mutual Funds
- Debt Mutual Funds
- Hybrid Funds
Equity Mutual Funds:
Equity oriented mutual funds where majority of the assets are invested in stocks. To broadly distinguish the Equity and non-equity oriented funds, the income tax department has come up with a definition of equity oriented funds. To qualify as equity oriented fund, the said mutual fund should have invested 65% of average annual net assets in Indian listed equities directly. Any other fund which doesn’t come under this definition would be considered as non-equity fund/debt fund for the purpose of taxation.
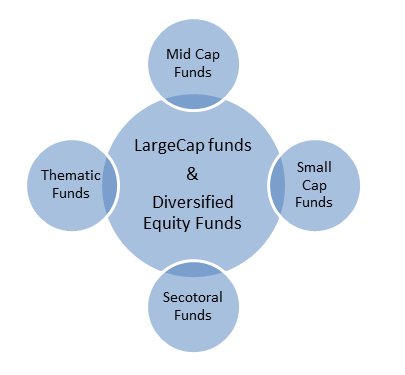
Types of equity mutual funds :
- Large cap fund
- Mid cap fund
- Small cap fund
- Diversified Equity Funds
- Sectoral funds
a. Large cap funds: Money collected under this fund is invested in large sized companies. The size of the company is defined based on the market capitalization (Market Capitalization = no of shares issued by the company X market price per share) of the company. There is no standard definition to categorize the companies based on the size. However, one way of categorizing the companies could be top 50 stocks listed in BSE/NSE are called as “Large Cap”. The other way of categorizing large cap stocks could be, any stock with a market capitalization beyond Rs. 10,000 crs.
Some of the large cap companies are Tata Consultancy Service, Reliance Industries, Sun Pharma, ONGC, Infosys, ICICI Bank etc. Large cap stocks are generally considered as a safe but because of this fact they are less volatile.
b. Mid Cap Funds: The stocks selected by the fund manager for this category of funds are generally considered as future leaders. One way of identifying mid cap stocks could be 150 stocks beyond large cap stocks are considered as mid cap. Other school of thought defines Mid-cap stocks with a market capitalization between Rs. 2000 – Rs. 10,000 crs. Since the mid-sized companies are not fully grown into large sized companies, these stocks have higher growth potential when compared to large cap stocks. Because of this, mid-cap stocks tend to outperform in bullish markets and vice versa.
c. Small Cap Funds: Stocks with market capitalization of less than Rs. 2000 crs is considered as small cap. They are in the large numbers compared to large and mid-cap, hence making the life of a fund manager difficult in choosing the right set of the stocks for the portfolio.
"Catch them young": Small cap stocks carry great potential for multi bagger returns in the long run; it’s like identifying Infosys stock at the initial stages of the company life cycle. But small cap stocks tend to be more volatile compared to Large and Mid-cap stocks and perform only at specific market cycles. Because of this nature, small cap stocks are considered to be riskiest among the three categories.
d. Diversified Equity Funds: The portfolio of Diversified equity funds is a combination of Large, Mid and Small cap stocks. Majority of the assets in the fund would be invested into Large cap stocks. There is no set standard allocation which diversified equity funds follow; every fund manager would have specific strategy for managing the fund.The other funds like “Opportunities Funds” also come under the category of diversified equity funds.
During the bearish phase of the market, a diversified equity fund might invest 85% of the corpus into Large Cap stocks and balance 15% would be allocated between Mid & Small Cap stocks. The fund manager would take a moderate aggressive stand in the bullish market by investing 75-80% in Large Cap and the rest in Mid and Small cap stocks.
Diversified equity funds would give stability and consistency of large cap funds by investing predominantly in Large cap and the Mid & Small Cap stocks would act as a returns booster to the portfolio.
e. Sectoral Funds: As the name suggests, the money collected under this fund invests in a specific sector for eg: Pharmaceutical, Banking, FMCG etc. Sectoral funds are considered as riskiest funds in equity mutual funds category, because the performance of different sectors is cyclical in nature. Not all the sectors perform at the same time. At any given point of stock market cycle different sectors tend to perform.
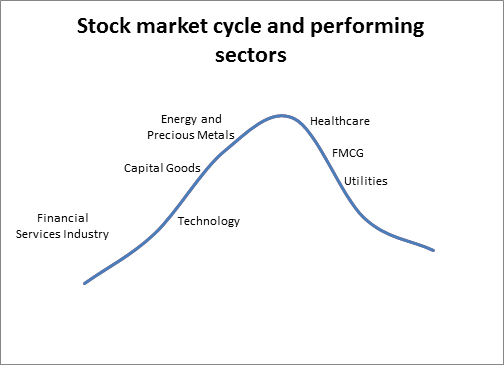
To make the best out of sectoral funds, an investor would have to enter the fund at the right time.
Risk – Return trade off of Equity funds:
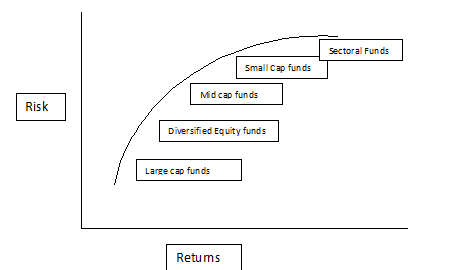
Positioning of Equity Mutual Funds: There are no set rules for creating a portfolio of equity funds; ideally the portfolio creation should happen with the help of the expert called as financial advisor. He would understand the customer and based on the needs, the portfolio would be suggested.
The basic thumb rule which an investor could follow is having a “Large Cap fund” and a “Diversified Equity Fund”. These two are an essential element in every portfolio. These two funds are like all season products which one should invest in.
Keeping the above mentioned point in mind, the equity investment portfolio could be divided into two parts:
1. Core Portfolio: This is an all season portfolio. 70-80% of the equity investment should ideally go into core portfolio. The overall risk is lesser and generates consistent return to the portfolio. The Core portfolio should ideally consist of existing Large Cap and Diversified Equity Funds with a longer track record. In some cases where the investor has a longer investment horizon, he could take exposure to Mid cap funds as well.
The funds selected and invested in are generally for a longer investment horizon and this portfolio doesn’t go through constant changes.
2. Satellite Portfolio: This portfolio changes as per the seasons and flavors. Active management is involved in handling this portfolio. 20-30% of the equity investments could go into this portfolio. Mid &Small cap funds, Small cap funds, Sectoral and Thematic funds should be part of this portfolio. Even new funds offered could be a part of this portfolio as well.